Awkward Tightness in the Legs? It May Be Compartment Syndrome

The most common area of the body in which runners complain of pain is the lower leg. Of course when you think about the mechanics of running, the lower leg receives the majority of the impact since it carries the most weight throughout the running cycle. This is why conditions such as knee pain, and more commonly plantar fasciitis are frequent. One of the more misdiagnosed conditions seen in recreational runners and elite athletes is chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS). During exercise blood flow increases and muscles expand. The pain from CECS is felt when the lower leg areas become swollen during exercise, if the fascia, which is basically a sheath that wraps around the muscles, does not expand with the muscles.
Symptoms
The type of pain usually felt with CECS is aching or burning in a specific area of the lower leg that begins at a certain time after beginning activity. Most commonly, the pain occurs in both legs and either in the posterior compartment (calves) or anterior compartment (shins). Along with pain, numbness or tingling, as well as tightness can be felt that worsens as you continue the exercise. These symptoms usually subside within 10 to 20 minutes after stopping the activity.

Differential Diagnosis
The reason this condition is misdiagnosed is because it resembles other more common conditions such as shin splints and tibial stress fractures. Shin splints are caused by overuse of the muscles connected to the shin bone, causing small tears which result in the muscle being “pulled” off the bone. The pain from shin splints is felt along most of the shin bone, whereas a tibial stress fracture is felt at a localized point in the bone. Both of these conditions, along with CECS, result in pain in similar areas and are usually caused by either improper biomechanics or overuse from adding mileage or intensity too soon during training.
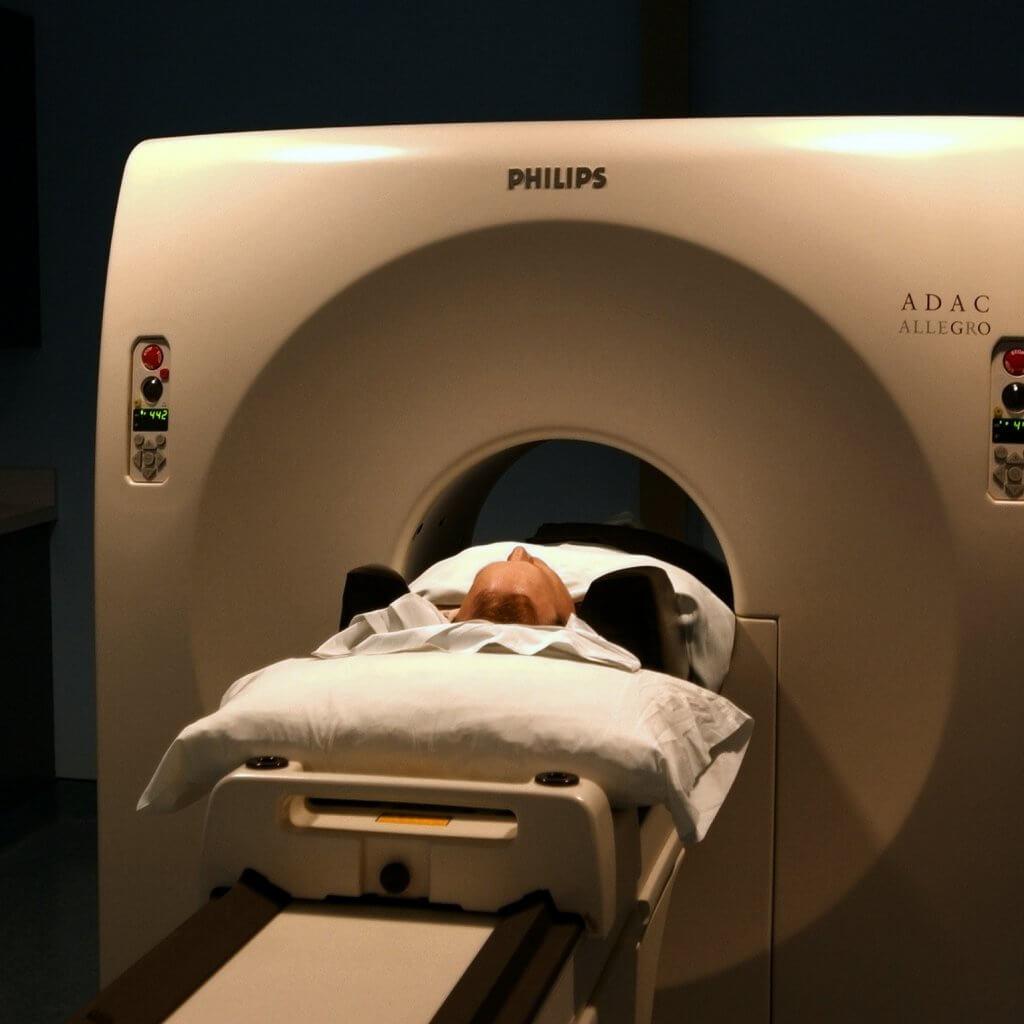
If you are experiencing pain during exertion, especially if it begins within the first 10 to 20 minutes of a run and relieves within 10 to 20 minutes after stopping, get evaluated by a professional. If along with the pain is a sensation of significant tightness in the lower legs, CECS is most likely expected. An MRI will help rule out specific muscular issues. There are newer, more advanced MRI exams that can assess how much fluid accumulation there is in the compartments of the lower leg during activity. This has been found to be accurate in diagnosing CECS. It may limit the need to use the more invasive approach of diagnosing which is compartment pressure testing where needles are inserted into the muscles to evaluate the amount of pressure present.
Treatment
The goal of treating CECS is to relieve the pressure in the affected compartment during exertion. Unfortunately, the first step in treatment is avoiding aggravating activities, such as running. Doctors may prescribe NSAIDs and an icing regimen to help decrease the inflammation. During this rest time from activity, it is effective to include techniques to keep the muscles and fascia flexible such as massage and stretching. Once the symptoms are more controlled, it is important to ease back into running VERY gradually to be able to monitor returning symptoms. As you do this, strengthening all lower leg muscles, including the feet, should be incorporated.
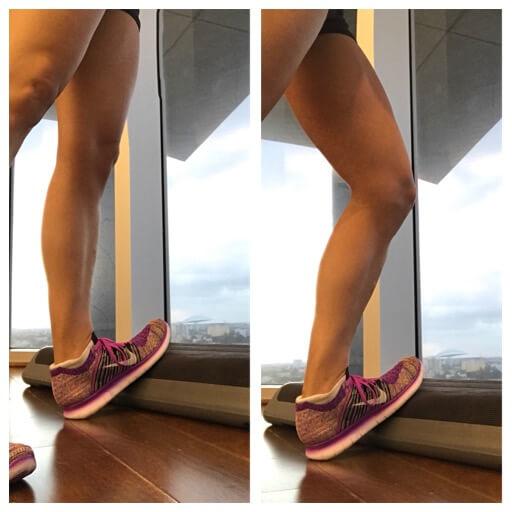
As shown below calf stretching should include performing with the knee straight, to stretch the outer muscles, and bent to stretch the deep soleus muscle.
The simplest way to keep the anterior dorsiflexors (along the shin) loose, is to use the foam roller or other deep tissue massage, as shown in the photo below.
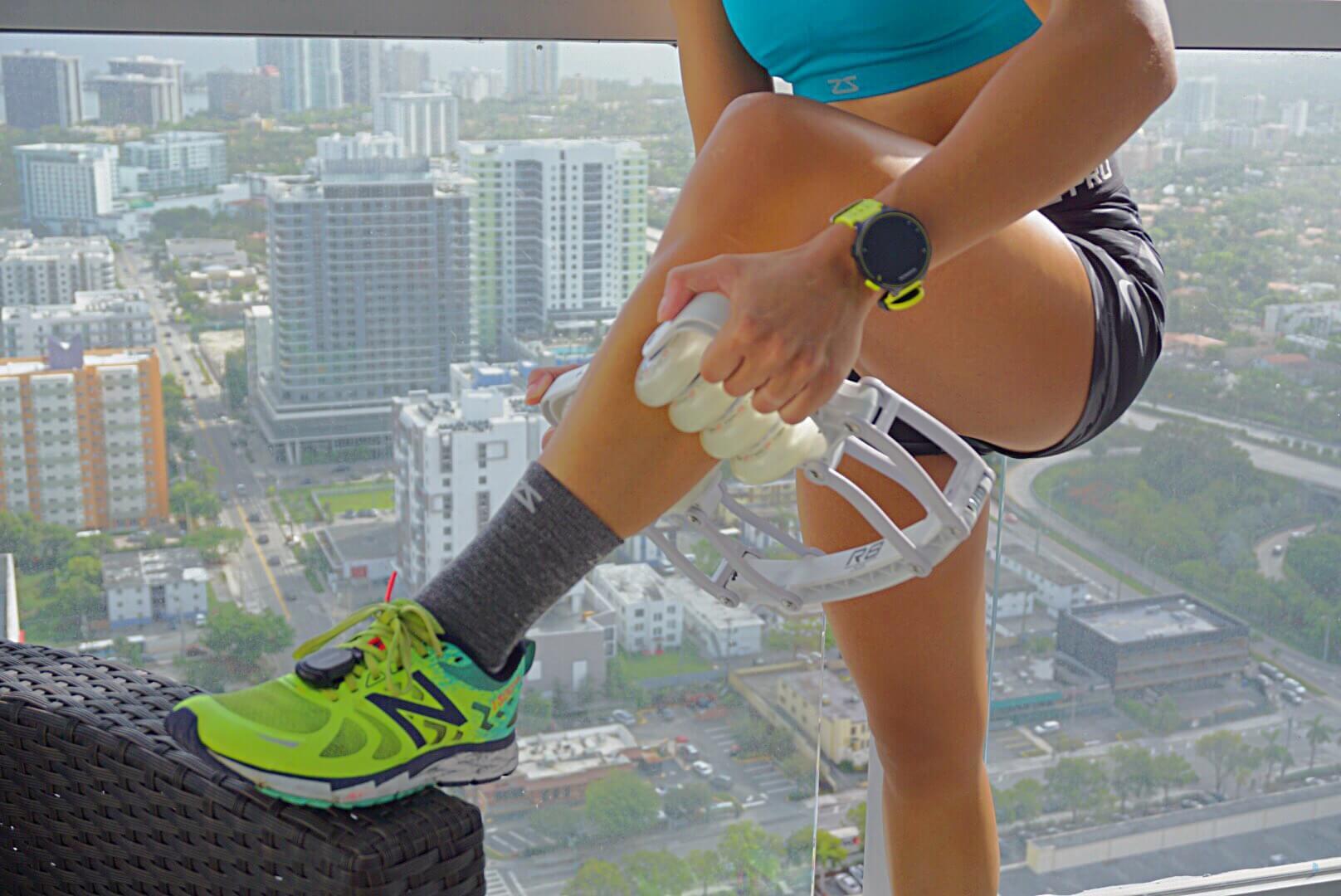


The first exercise most athletes include for the lower leg are basic heel raises. As mentioned above, the calves also include a deeper muscle called the Soleus, that often lacks sufficient strength. You can target these muscles by performing the heel raise exercise with a bent knee, or sitting adding weight to your lap.
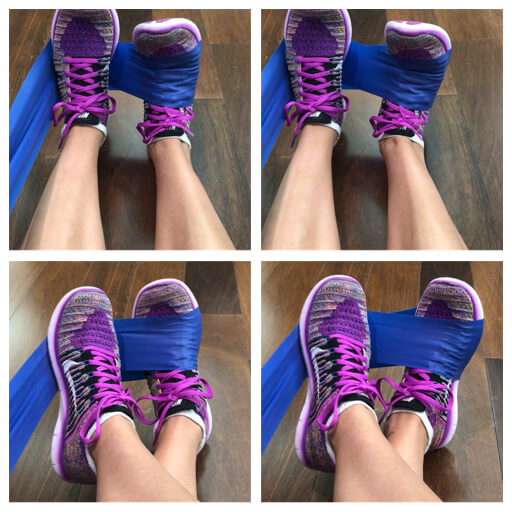
Weakness in the ankle and foot may also contribute to lower leg issues. To target these ankle and foot stabilizers, using a resistance band is effective. Other exercises include single leg standing on a stable and unstable surface such as a foam mat or balance disc.

Unfortunately, in the majority of the more severe cases, a surgical procedure, called a fasciotomy, is required. Basically the fascia itself is cut open to relieve the tension in order to allow normal blood flow and muscle expansion to cause less pressure during activity. The recovery time after this procedure is quite short and allows athletes to return to their sport within 6 to 12 weeks. Post-surgical rehabilitation requires the same treatment as the conservative approach mentioned above.
Prevention & Maintenance
Biomechanics, or running form, is commonly blamed for lower leg dysfunction, such as CECS. Research has been done on evaluating foot strike patterns in runners and how these patterns may cause mechanical issues in joints from the lower leg to the hip and spine. When one uses the heel strike for landing during running, the anterior compartment muscles, the dorsiflexors, must act eccentrically to control the foot from slapping onto the ground with every step. This causes overuse and inflammation in the area. Many studies have evaluated the outcome of changing this foot strike pattern to a mid-foot or forefoot landing, and have concluded positive results in CECS symptoms. This is a change that should be done gradually, such as beginning with 5 minutes of forefoot strike in a single run and adding 5 minutes every few runs.

Another prevention option is running with shoes and/or orthotics that limit pronation of the foot. Overpronating requires even more work for the dorsiflexor muscles and causes increased tightness to the entire lower leg compartment muscles.
The exercises mentioned above should be incorporated to help prevent CECS and other lower leg dysfunction, as many times weakness and inflexibility are the cause. If you have been diagnosed with CECS or are experiencing symptoms, make sure to back off of the aggravating activities and always ease back into it during recovery. Seek medical advice if symptoms do not resolve or become severe. Remember, the quicker you take care of your pain, the quicker you will be back to doing what you love.
Sources
- , Chronic Exertional Compartment Syndrome of the Leg, Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine
- , Common Leg Injuries of Long-Distance Runners: Anatomical and Biomechanical Approach, Sports Health
- , Chronic Exertional Compartment Syndrome and Forefoot Striking: A Case Study, International Journal of Athletic Therapy & Training
Latest Articles
 Is Running on a Treadmill Easier Than Running Outside?Runners have their own preferences, whether it is treadmill running, running outside on the road, or exploring trails. So...
Is Running on a Treadmill Easier Than Running Outside?Runners have their own preferences, whether it is treadmill running, running outside on the road, or exploring trails. So... Is It OK to Use Trail Running Shoes on the Road?While trail running shoes can be used on roads, especially in situations where a runner encounters mixed terrains or pref...
Is It OK to Use Trail Running Shoes on the Road?While trail running shoes can be used on roads, especially in situations where a runner encounters mixed terrains or pref...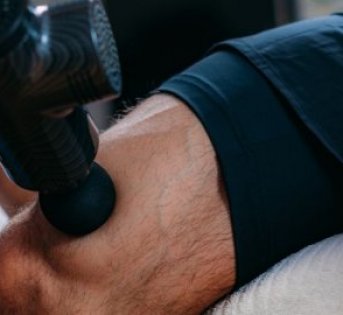 How to Fix Sore Quads After Running?Rest, ice, gentle stretching, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help soothe sore quads after running. Also, ensure ...
How to Fix Sore Quads After Running?Rest, ice, gentle stretching, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help soothe sore quads after running. Also, ensure ... 10 Fruits With The Most Electrolytes to Replace Sports DrinksThese fruits are high in electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium, essential for hydration, muscle function...
10 Fruits With The Most Electrolytes to Replace Sports DrinksThese fruits are high in electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium, essential for hydration, muscle function...

